GCA’s Digital Transformation: Innovative Solutions for Recommendation Implementation and Audit Follow-up
By Mr. Ahmed AlQurashi, CPA, Assurance Director at the Supreme Audit Institution of Saudi Arabia

Introduction
In recent years, the General Court of Audit (GCA), Saudi Arabia’s Supreme Audit Institution (SAI), has undertaken measures to bolster its framework, aiming to elevate its oversight capacity with a focus on objectivity, efficiency, and professionalism. Embracing a proactive stance, the GCA is committed to adapting to the swift evolution in financial auditing and performance oversight. GCA leveraged a modern technologies and methodologies to conduct audits with heightened effectiveness and quality, ensuring alignment with contemporary standards and practices. On the other hand, government agencies and ministries within the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia’s public sector have also undergone significant transformations in recent years. These efforts are aligned with the ambitious goals outlined in Vision 2030 of the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia, which aims to diversify the economy, enhance public sector efficiency, and promote sustainable development. (1)
In response to the dynamic shifts and challenges facing the auditing landscape, GCA has embarked on a strategic initiative focusing on digital solutions under the visionary leadership of His Excellency Dr. Hussam Alangari.(2) This framework, characterized by streamlined communication, centralized tracking, and integrated data analysis tools, not only facilitates efficient audit follow-up procedures and recommendation implementation, but also fosters transparency, accountability, and continuous improvement in public sector operations.
The data regarding the effectiveness of GCA’s framework in developing and implementing recommendations and audit follow-up, along with its impact on improving government programs, was collected through a survey. The survey was distributed to a total of 141 participants, consisting of employees of the GCA (60) and GCA’s auditee (81). The survey Questionnaires and their answers are shown in Annex 1 and Annex 2.
Develop recommendations through the audit process:
While there are key techniques for conducting audit follow-ups, including establishing communication channels, setting targeted follow-up deadlines, utilizing tracking sheets, conducting site visits and meetings with those charged with governance and stakeholders, it is important to highlight the central role played by introducing the Shamel Portal within GCA. At the forefront of this transformative endeavor is the Shamel Portal, a digital platform aimed at automating the work of GCA. It offers a digital solution that combines techniques for implementing recommendations that have been identified post-audit and for conducting audit follow-ups, thereby enhancing efficiency and utilization. Shamel has enhanced GCA’s capability of improving audit follow-up procedures and implementing recommendations through the audit process as the following:
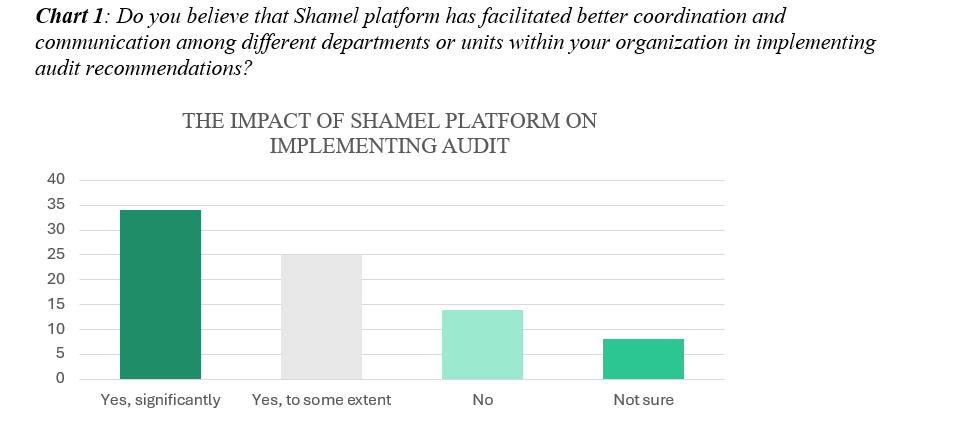
- Streamlined Communication: Shamel facilitates the exchange of audit-related data between stakeholders within audited entities, enhancing communication channels. This ensures that recommendations and follow-up actions are communicated efficiently and effectively. Chart 1 illustrates that Shamel has significantly improved GCA’s capacity for enhancing interdepartmental coordination and communication in implementing audit recommendations. Among GCA’s auditees surveyed, the majority (74%) reported a significant positive impact of Shamel, with only 17% indicating no impact and 10% expressing uncertainty.
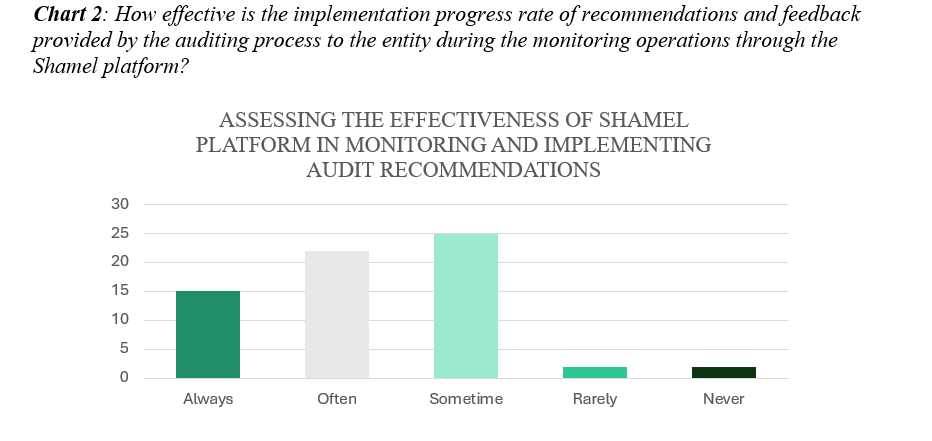
- Centralized Platform: By providing a single platform for audit-related activities, Shamel simplifies the process of tracking recommendations and follow-up actions. Auditors can easily monitor the status of recommendations and follow-ups, ensuring timely implementation. According to the data presented in Chart 2, 94% of respondents perceive the Shamel platform as more often effective in implementing recommendations and feedback during monitoring operations. This high efficacy is attributed to key features of Shamel, including its effectiveness, efficiency, and reliability, which have played a pivotal role in GCA’s successful implementation of audit recommendations.
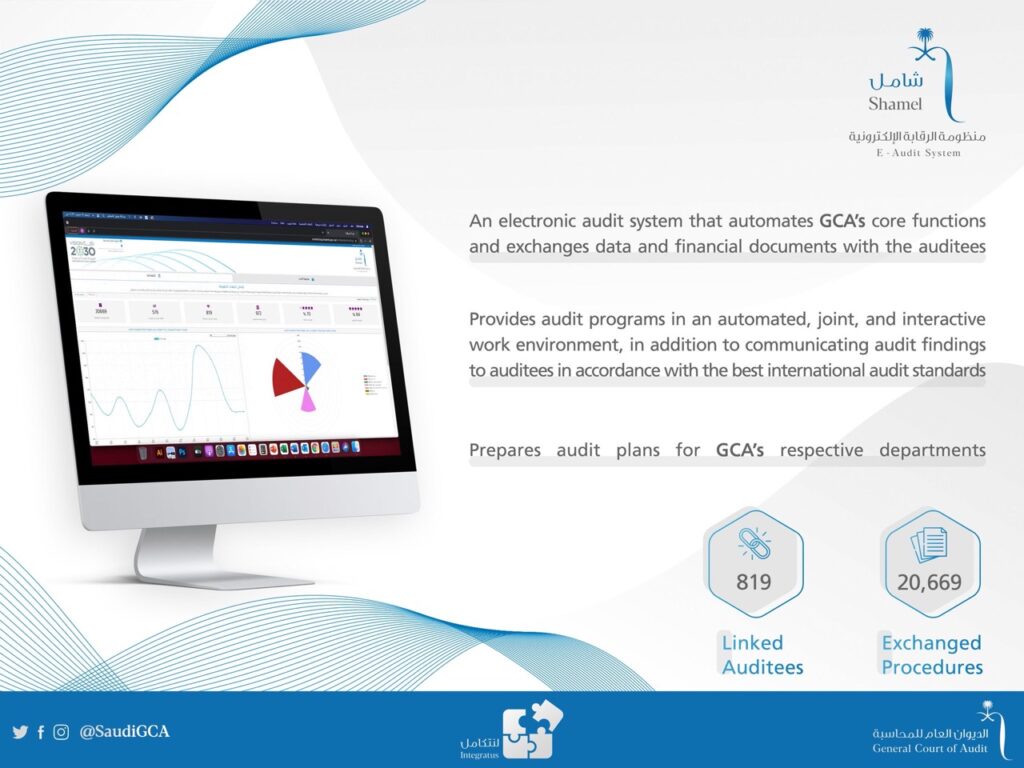
- Integration and Training: The integration of over 800 auditees into the Shamel system is complemented by comprehensive training sessions. This proactive approach underscores a commitment to engaging auditees in the audit process, fostering a culture of collaboration, transparency and accountability. Ensuring that all stakeholders are proficient in utilizing the platform effectively empowers auditees to actively participate in the audit process and take ownership of implementing recommendations.
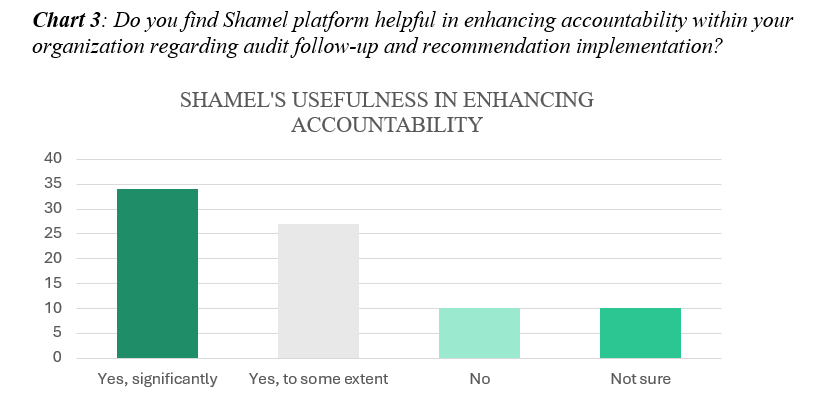
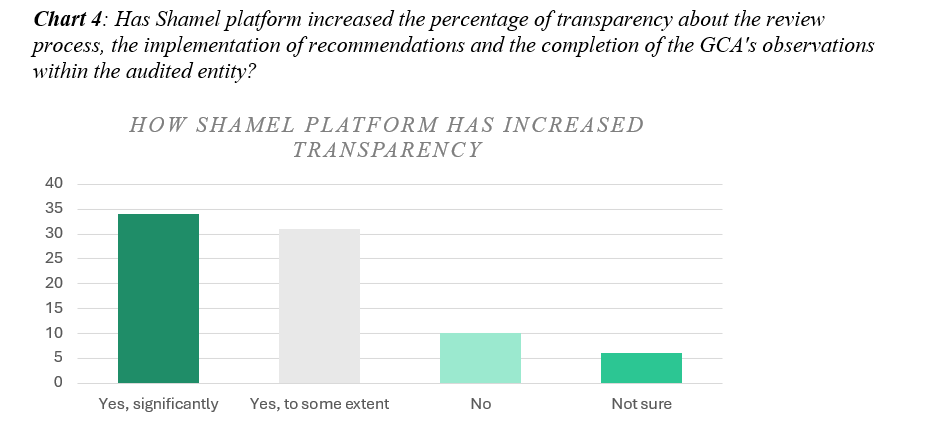
Shamel portal introduces advanced data analysis tools, empowering the audit team to leverage data-driven insights in evaluating the performance of audited entities. In addition to data analysis capabilities, Shamel introduces an interactive portal designed to streamline communication and collaboration with respect to the audit findings between the audit team and audited entities. Chart 3 and Chart 4 highlight the enhanced accountability, transparency, and streamlined communication facilitated by Shamel among audited entities. In Chart 3, 76% of respondents noted that the platform has improved accountability regarding recommendation implementation and observations fulfillment by the GCA. Only 12% found it ineffective, with 12% unsure. Chart 4, on the other hand, depicts that most audited entities (65 out of 81) believe that Shamel promotes transparency within their organization regarding the review process and implementation of recommendations. However, some audited entities (10 out 81) believed that Shamel did not have any impact on transparency, while other entities (6 out of 81) were unsure of Shamel’s impact on transparency within their organization.
Follow up and correspondence with government agencies and ministries to track recommendation implementation:
Follow-up and correspondence with government agencies and ministries to track recommendation implementation are pivotal aspects of audit oversight, facilitated significantly by the Shamel platform.
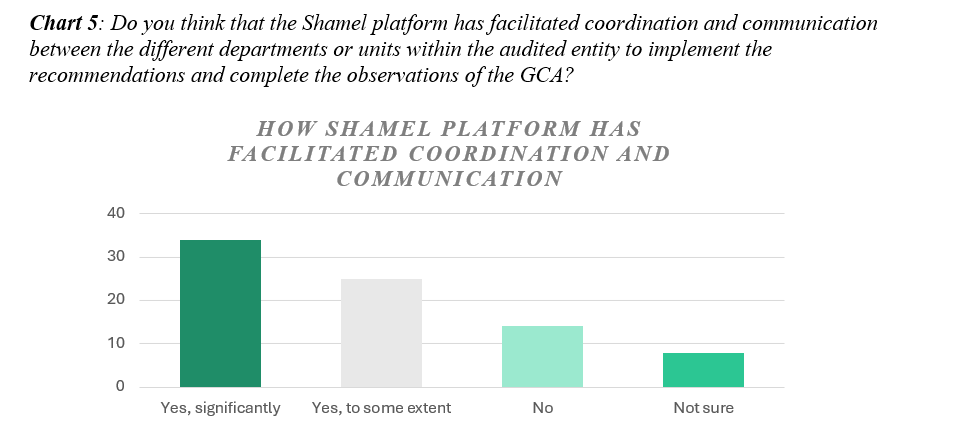
- Facilitating Coordination and Communication: Shamel serves as a multifaceted tool between the General Court of Audit (GCA) and government entities. The platform’s built-in communication tools enable efficient correspondence, updates, and clarification requests regarding recommendation implementation efforts. As shown in Chart 5, majority of audited entities (59 out of 81) reported that Shamel has been useful in facilitating coordination and communication between the different departments or units within the audited entity to implement the recommendations and complete the observations of the GCA. Government agencies and ministries including those charged with governance can provide feedback, request guidance, or seek clarification on specific recommendations directly through the platform. 14 out of 81 entities reported that the platform has had no impact in facilitating coordination and communication within their organization, while 8 out of 81 were not sure.
- Task Management and Progress Tracking: Shamel’s task management functionality empowers the GCA to assign responsibilities, set deadlines, and monitor the status of recommendation implementation tasks. Furthermore, the platform offers comprehensive indicators and detailed data to assess performance, while also displaying GCA’s notes and observations in a clear and accessible manner. This functionality ensures that recommendations are effectively implemented and resolved in a timely manner. By offering a comprehensive view of each task’s status, Shamel promotes proactive management and continuous improvement, enhancing accountability and efficiency.
- Reporting and Insights: Shamel’s reporting capabilities generate comprehensive progress dashboards on recommendation implementation efforts, providing stakeholders with clear insights into each recommendation’s status, progress, and remaining tasks. Through its integrated features and user-friendly interface, Shamel enhances transparency, accountability, and efficiency in the follow-up process, ultimately contributing to improved governance and public sector performance.(3)
Identify the impact of how government programs are improved through recommendation implementation:
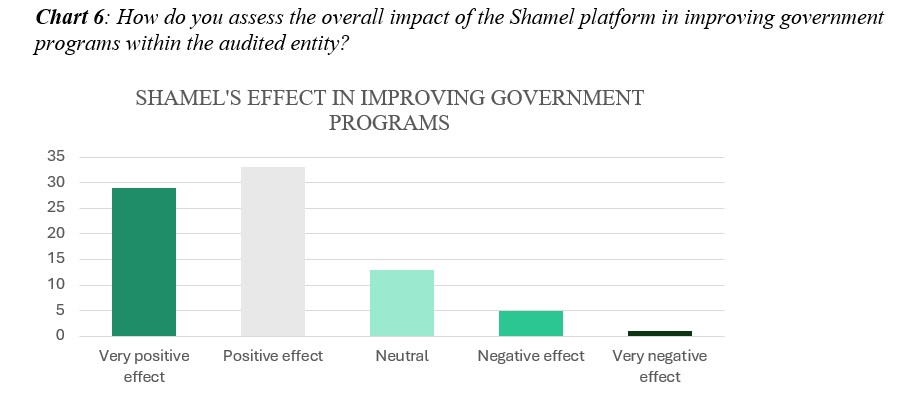
As shown in Chart 6 above, the implementation of recommendations following audits conducted through the Shamel platform has yielded remarkable improvements in government programs. 77% of the audited entities that participated in the survey reported that Shamel has significantly led to improvement of government programs within their organization. Conversely, only a 7% indicated a negative effect, while 16% remained neutral. His Excellency Dr. Hussam Alangari, President of GCA, emphasized Shamel’s achievements in facilitating the effective enhancement of government programs through seamless data and document exchange between parties, alongside automated reporting of audit results and comprehensive visibility into observations and their corresponding performance indicators. This integration not only expedites the audit process but also ensures effective communication and monitoring of recommendations, reflecting the GCA’s commitment to quality and efficiency in oversight procedures.(4)

Conclusion
In conclusion, the utilization of the Shamel platform represents a transformative step forward in the realm of audit oversight and recommendation implementation within government agencies and ministries. By fostering seamless communication, facilitating task management, and providing valuable insights through comprehensive reporting, Shamel significantly enhances the efficiency and effectiveness of the audit process as well as its role in promoting transparency and accountability underscores its importance in improving governance and optimizing the allocation of public resources.
Bibliography
GENERAL COURT OF AUDIT (GCA). “THE GENERAL COURT of AUDIT ”a New Era … With a Vision Full of Ambitions”.” https://www.gca.gov.sa/Uploads/Documents/Introductory.brochure.pdf, 2023.
Saudi Vision 2030. “Saudi Vision 2030 Overview.” www.vision2030.gov.sa, 2016. https://www.vision2030.gov.sa/en/vision-2030/overview/.
General Court of Audit. (2024, March). The President of GCA Inaugurates Electronic Audit System (Shamel 2.0). Retrieved from https://www.gca.gov.sa/NewsDetails?id=2397&callback=1&lang=en





